As most people already know, bones protect the body from mechanical damage. For example, the skull protects the brain, and the rib cage protects the internal organs. Bones also serve as levers for the muscles attached to them, thereby multiplying the force of the muscles to attain movement (Gartner H, 2007).
Bone is a material that has the same strength as cast iron, yet achieving this while remaining as light as wood. Bones are a reservoir for several minerals of the body; for example, they store about 99% of the body’s calcium and 85% of the phosphorus (Lian J. 2004)
Bone Structure
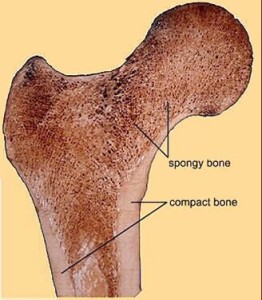
Two types of bones in our body are: compact bone and spongy bone.
Compact bone is the hard material that makes up the shaft of long bones (e.g. limb bones such as the humerus or femur) and the outside of other bones. Compact bone consists of cylindrical units called osteon. Osteon contains bone cells. It surrounds the canals for blood vessels and nerve fibers. These canals are important to connect the blood vessels for fine nutrients and waste exchange within the bones. Infection, fracture, or abnormal mechanical load may damage the canals and result in irritation in adults or malformation in children.
Spongy bone consists of thin, irregular-shaped plates. This is made mainly of collagen, and therefore is lighter, softer, and weaker than compact bone. It is usually found at the end of long bones and joints. It provides the growth plates during the teenage years and is the site for red blood cell formation in adults (Dowshen S, 2015) .
Unfortunately, bone structure deteriorates, and bone mass becomes low as calcium and water content in the bone decrease with age. This condition is called osteoporosis, and is the most prevalent bone disease in Canada. In addition, bones contain a central cavity, the marrow cavity. This cavity houses the bone marrow which is responsible for creating blood cells.
Others…
Ligament is tissue that connects bones to other bones to form joints. It is a band of connective tissue consisting of collagen fibers. It usually limits excessive mobility and prevents dislocation at the joints. If the ligament is dramatically stretched or torn off, the joint become unstable, resulting in joint instability or sprain.
Synovial membrane is the soft tissue found in mobile joints such as hip, shoulder and knee joints. This membrane produces synovial fluid that reduces friction between cartilage. Inflammation of the synovial membrane is usually associated with osteoarthritis. Inflammation will cause the joint to swell, become warm and painful, eventually leading to degeneration of the joint.